Composting Materials
Key Takeaways
- Composting is a natural process of recycling organic material.
- Materials for composting are categorized into green and brown.
- Proper ratios of green to brown materials enhance compost quality.
- Common kitchen and garden waste can be composted easily.
- Understanding what can and cannot be composted is crucial for effective composting.
Composting is an incredible way to turn waste into valuable compost that can enrich your garden. In this guide, we'll explore what materials are best for composting, how to categorize them into green and brown materials, and tips for successful composting. Let's dive in!
What is composting?
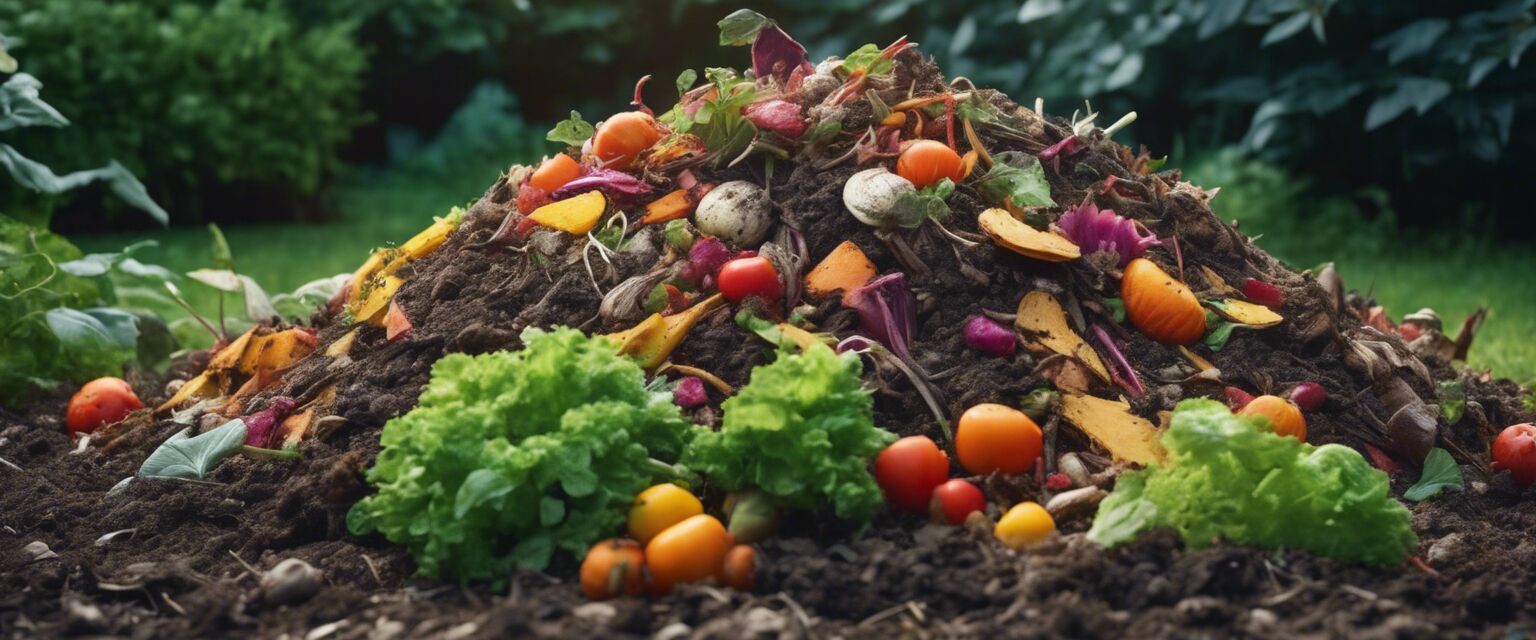
Composting is the process of turning organic waste into nutrient-rich soil conditioner. It involves the decomposition of materials by microorganisms, making it a fantastic way to recycle kitchen scraps and yard waste.
Types of composting materials
Composting materials can be divided into two main categories: green materials and brown materials. Understanding these categories can help you create a balanced compost pile.
Green materials
Green materials are rich in nitrogen and are typically fresh, moist, and vibrant in color. Hereâs a list of common green materials:
| Green Materials |
|---|
| Vegetable scraps |
| Fruit scraps |
| Grass clippings |
| Coffee grounds |
| Eggshells |
| Fresh leaves |
| Plant clippings |
Brown materials
Brown materials are high in carbon and are dry and brown in color. They help balance out the nitrogen-rich green materials. Hereâs a list of common brown materials:
| Brown Materials |
|---|
| Dried leaves |
| Cardboard |
| Newspaper |
| Sawdust |
| Straw |
| Wood chips |
| Egg cartons |
Ideal ratios for composting
To create effective compost, it's crucial to maintain the right ratios of green and brown materials. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a ratio of about 2:1 or 3:1 of brown to green materials.
Example composting ratio
Hereâs a simple table to illustrate the ideal composting ratio:
| Green Materials | Brown Materials |
|---|---|
| 1 part (e.g., 1 bucket of vegetable scraps) | 2 parts (e.g., 2 buckets of dried leaves) |
| 1 part (e.g., 1 bag of grass clippings) | 3 parts (e.g., 3 bags of cardboard) |
Materials that should not be composted
While many materials can be composted, some should be avoided to prevent issues. Here's a list of materials to avoid:
- Meat and fish scraps
- Dairy products
- Oils and fats
- Pet waste
- Diseased plants
- Weeds that have gone to seed
- Chemically treated wood
Tips for successful composting
Beginners section
- Start small: Begin with a small compost bin to practice.
- Keep it moist: Make sure your compost pile is moist but not soggy.
- Turn the pile: Aerate your compost by turning it every few weeks.
- Monitor temperature: A hot compost pile breaks down faster.
- Be patient: Composting takes time; usually several weeks to months.
Conclusion
Composting can be a simple and rewarding way to reduce waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your plants. By understanding the types of materials you can compost and following the tips provided, you'll be on your way to a successful composting experience.
Learn more about composting
If you're interested in exploring more about composting, check out our sections on Compost Tumblers, Indoor Compost Bins, and Worm Composting Kits. Happy composting!